It’s been said that Hollywood is more an idea than a place, and no task punctuates the notion quite like asking people to choose the best Hollywood book of all time: “What do you mean,” they inevitably ask, “by ‘Hollywood’?”
The list that follows, compiled from a survey of experts in the worlds of publishing and entertainment and written by regular contributors to The Times’ film and books coverage, answers that question more astutely than I ever could. In fiction and non-, across genres and decades, these 50 titles compare Hollywood to an assembly line, a criminal enterprise, a high-seas expedition and much, much more — a penchant for shape-shifting that might explain its hold on the cultural imagination.
Yet any entity that can simultaneously be described as an industry, a society, even a style, is liable to collect more detractors than it would had it remained simply a real estate development, and if there’s a through-line in the great Hollywood books it is the conviction that creating magic must come at a cost. Sometimes comic, more often tragic, they chronicle disappointments, humiliations, botch-jobs and flops of every conceivable variety, personal and professional, creative and economic, individual and institutional; even the more rose-colored perspectives still make it seem as if producing a single movie, much less a good one, qualifies as a miracle.
But that, I suspect, is why we keep coming back, self-flagellants before the altar of motion pictures. This place, this idea, demands of its adherents what religion does any pilgrim — devotion, sacrifice, faith that all will be worth it in the end — and supplies in turn the same benefits — ritual, community, comfort. You simply have to take it on trust: If watching movies is heaven, and living without them is hell, then Hollywood is the purgatory in between. —Matt Brennan

Subscribers get exclusive access to this story
We’re offering L.A. Times subscribers special access to our best journalism. Thank you for your support.
Explore more Subscriber Exclusive content.


Movies (and Other Things)
(Shea Serrano, 2019)

There’s a nonchalant freshness to the way former journalist and author Serrano writes about the variety of subjects that interest him, whether basketball or movies. His entertaining and insightful musings on the latter form the uniquely titled chapters here: Each of them aims to provide answers to one of Serrano’s specific inquiries related to popular flicks. The approachable tone, and the selection of films discussed, removes any sense of snobbery that some readers may associate with film criticism. Serrano doesn’t purport to be an expert but rather a movie fan, one with a talent for crafting engaging prose, sharing his most galaxy-brained thoughts on the kind of movies one has seen more times than they can count. — Carlos Aguilar

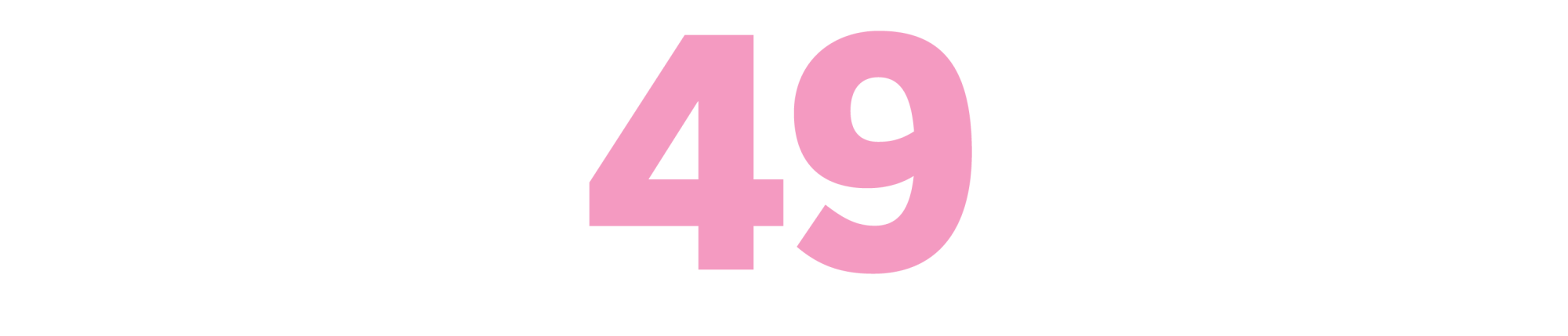
Myra Breckinridge
(Gore Vidal, 1968)

Vidal’s 1968 tale of a trans woman exacting her revenge on a Hollywood studio is campy and profane, its exclamatory prose giddy to provoke. Written in a haste that contrasted Vidal’s more considered historical fiction, “Myra” reads like Vidal was in a mad dash to work through his own sexuality. (“A very subtle psychological self-portrait,” was Christopher Isherwood’s cheeky assessment.) But its heedless vigor is part of its enduring charm, sending up the egos and power plays (both financial and sexual) that drive the movie business. The book is probably best known for a dismal 1970 adaptation starring Raquel Welch and John Huston that remains bolted to lists of the worst-ever movies. But the novel itself remains a potent Tinseltown satire. — Mark Athitakis

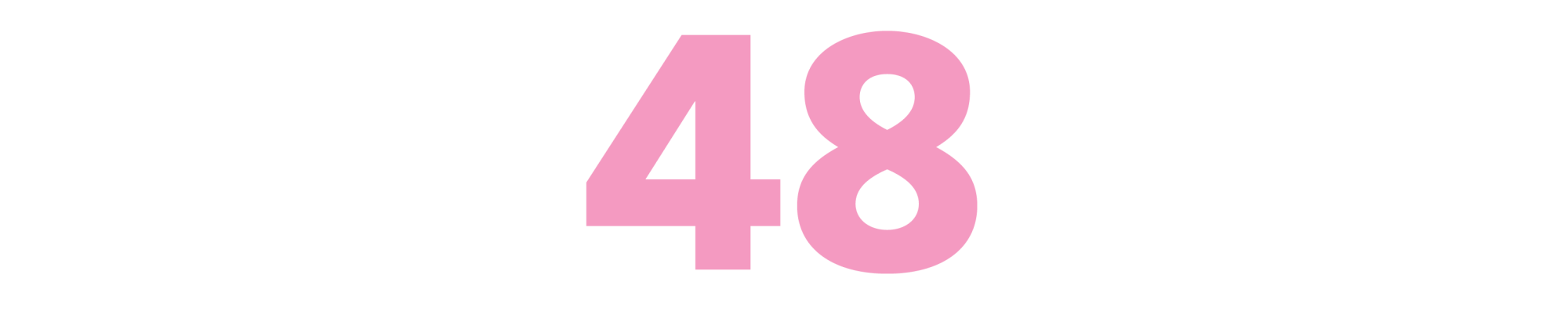
The Big Goodbye: Chinatown and the Last Years of Hollywood
(Sam Wasson, 2020)

No one has been more haunted by the fateful final line of Roman Polanski’s most accomplished work, “Forget it, Jake. It’s Chinatown,” than Wasson. To dissect a seminal work in American cinema, the author dived deep into the minds and lives of the key players that came together for this picture about corruption in 1930s Los Angeles to become what it is. These include star Jack Nicholson, Paramount executive Robert Evans, screenwriter Robert Towne and the controversial Polanski himself. As he maps the creation of “Chinatown” in astounding detail, Wasson simultaneously eulogizes the bygone era when Hollywood studios were interested in filmmaking with an idiosyncratic voice. — CA


Dead Stars
(Bruce Wagner, 2012)

Don’t look for someone to like in this blistering, X-rated takedown of Hollywood strivers. Not the pregnant teen who’s been exploited by her Nan Goldin-like mother since childhood or her porn-obsessed boyfriend. Not the paparazzo who strives for underage crotch-shots or the young cancer survivor who spells it with a K, hoping to get the attention of the Kardashians. Published in 2012, the text leaps, runs on, includes emoticons and ignores punctuation, just like DMs and text messages. In this massive, manic book full of explicit sex and characters with equally naked ambition, Wagner holds a mirror up to the underside of Hollywood. It may be a disturbing vision, but that doesn’t mean it’s not true. — Carolyn Kellogg

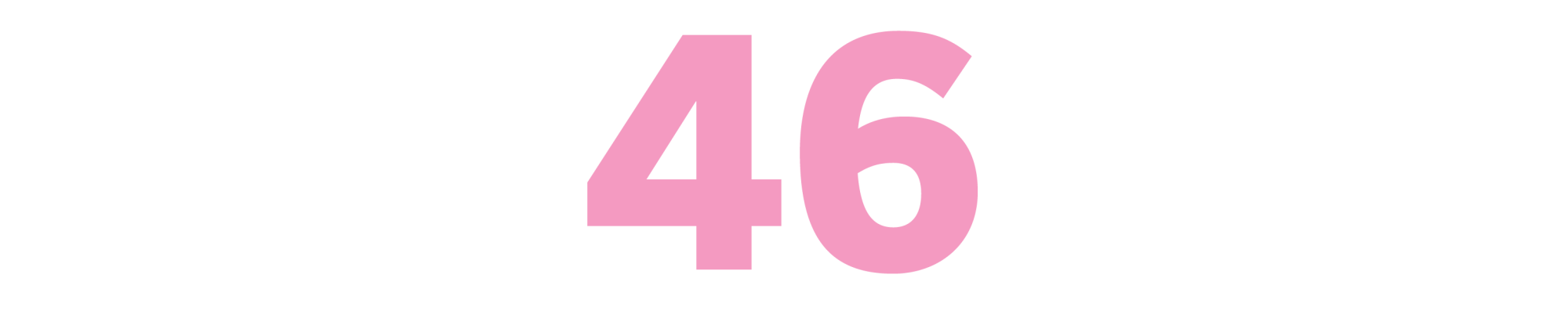
Arabs and Muslims in the Media: Race and Representation after 9/11
(Evelyn Alsultany, 2012)

At the heart of this erudite academic monograph is a counterintuitive claim: following the 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon, the rise of hate crimes and government policies that targeted Arabs and Muslims was met with an equally high incidence of sympathetic portrayals of those populations in the U.S. media. That’s not to say there weren’t horribly damaging depictions of Middle Eastern terrorists rooted in offensive racial stereotypes — many concocted in the service of offering up an “evil cultural Other” that anchored much of the rhetoric around the so-called War on Terror. But Alsultany’s study keenly avoids endorsement of neat categories like “good” and “bad” representation, aiming instead to complicate how it is that media images on either side of that divide can fuel meanings that end up justifying policies of exclusion and inequality. — Manuel Betancourt

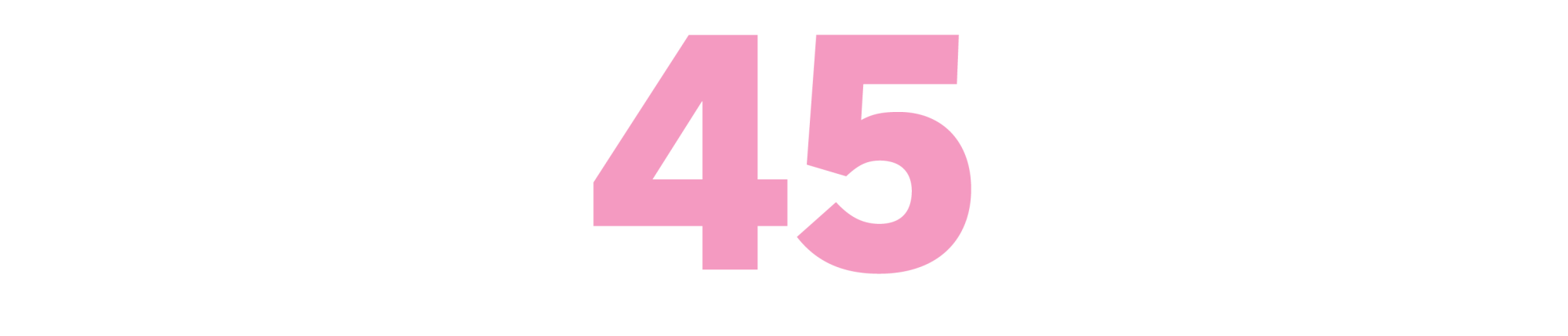
The Deer Park
(Norman Mailer, 1955)

Though set in Palm Springs, “The Deer Park” is the most insightful, unsparing look at the machineries of Hollywood I know of — Mailer’s underrated masterpiece.
— HOWARD RODMAN, novelist, screenwriter, former president of the Writers Guild of America West and current vice president, Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences

Everybody Thought We Were Crazy: Dennis Hopper, Brooke Hayward, and 1960s Los Angeles
(Mark Rozzo, 2022)

Hopper is the bold-faced name, but Hayward is the heart of this intimate story of a marriage that tied together the L.A. art and music scenes, Golden Era Hollywood and the emerging indie film movement. Hayward’s parents were so Old Hollywood that she and Hopper were regularly invited to David O. Selznick’s house; Hopper would, after their split, make “Easy Rider.” Before things fall apart, they hang with the Ferus Gallery and help Andy Warhol have his first L.A. art show; act and model and start a family; and play host to a glittering parade of soon-to-be-famous musicians and actors. Hayward is still with us and opened the door to tell the story of the time her bohemian, chaotic Hollywood home played host to a seismic shift in three art forms at once. — CK

Stay Tuned: An Inside Look at the Making of Prime-Time Television
(Richard Levinson and William Link, 1981)

Levinson and Link are hardly household names among today’s TV heads, but they deserve to be. As the creators of “Columbo” and “Murder, She Wrote,” and a library full of trailblazing TV movies (including “Crisis at Central High” and “That Certain Summer”), they combined razor-sharp storytelling instincts with an acute social consciousness at a time when television was still widely derided as “the idiot box” (or worse). They also wrote this shrewdly intelligent assessment of their work and their chosen field, a good two decades before the dawn of prestige cable and the widespread acceptance that the small screen is where the really good storytelling happens. The book’s title intentionally predicts great things on the horizon in the early ‘80s, when Levinson and Link wrote the book. They’re also low-key quite funny, as when they point out that the producer of any dramatic series might also indulge in some rewriting “if he’s a writer (or thinks he’s a writer).” — Chris Vognar

Making the White Man’s Indian: Native Americans and Hollywood Movies
(Angela Aleiss, 2005)

A rigorous study of how anti-Native racism and misrepresentation has pervaded Hollywood filmmaking, from D.W. Griffith shorts to “The Searchers,” “Stagecoach” to “Dances With Wolves,” one-note savages to white saviors. But Aleiss, who watched dozens of features and shorts for this influential book, also demonstrates that there were plenty of affirming stories about Native Americans in the pre-western era — “the Indian as a noble hero actually preceded the cowboy star,” she notes. But such stories were frozen out in favor of cowboys-and-Indians yarns, and shifting audiences throughout the 20th century influenced what kinds of Native American narratives were elevated and suppressed. Aleiss spotlights the industry groups and directors who’ve worked to address stereotypes about “half-breeds” and conversation narratives but also demonstrates why it’s often been a losing battle. — MA

Reel
(Kennedy Ryan, 2021)

“Reel” is a gorgeous romance novel about Broadway and Hollywood. Through Ryan’s masterful storytelling, readers are transported into a world where passion, ambition and the pursuit of one’s dreams collide, leaving the characters to make difficult choices about love, family and the future.
— LEAH KOCH, co-owner of Culver City’s the Ripped Bodice, the first independent bookstore in the United States devoted to the celebration of romance novels


Raising Kane
(Pauline Kael, 1971)

Did Orson Welles get too much glory for “Citizen Kane”? Absolutely, New Yorker film critic Pauline Kael insists in this novella-length fire-starter about the making of the greatest movie of all time. (We can save that skirmish for another day.) As Charles Foster Kane, a sendup of newspaper tycoon William Randolph Hearst, Welles embodied the image of a vainglorious Great Man. But Welles’ success, according to Kael, meant he also needed to be taken down a peg. > GO TO STORY
Subscriber Exclusive Alert
If you're an L.A. Times subscriber, you can sign up to get alerts about early or entirely exclusive content.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.


Toms, Coons, Mulattoes, Mammies, and Bucks: An Interpretive History of Blacks in American Films
(Donald Bogle, 1973)

Donald Bogle’s “Toms, Coons, Mulattoes, Mammies, and Bucks” is considered the standard text on Black characters in American movies. But when the book was first published, in 1973, it was just about the only text on the subject. This might be hard to imagine today, when books about the intersection of race and cinema flow forth on a regular basis (among the strongest in recent years are Will Haygood’s “Colorization: One Hundred Years of Black Films in a White World” and Robin R. Means Coleman’s “The Black Guy Dies First: Black Horror Cinema From Fodder to Oscar”). Such abundance was unthinkable when Bogle, then a young journalist who had worked as a story editor for Otto Preminger, began his odyssey into the industry’s appallingly racist history. Bogle’s book was practically the birth of the field. > GO TO STORY

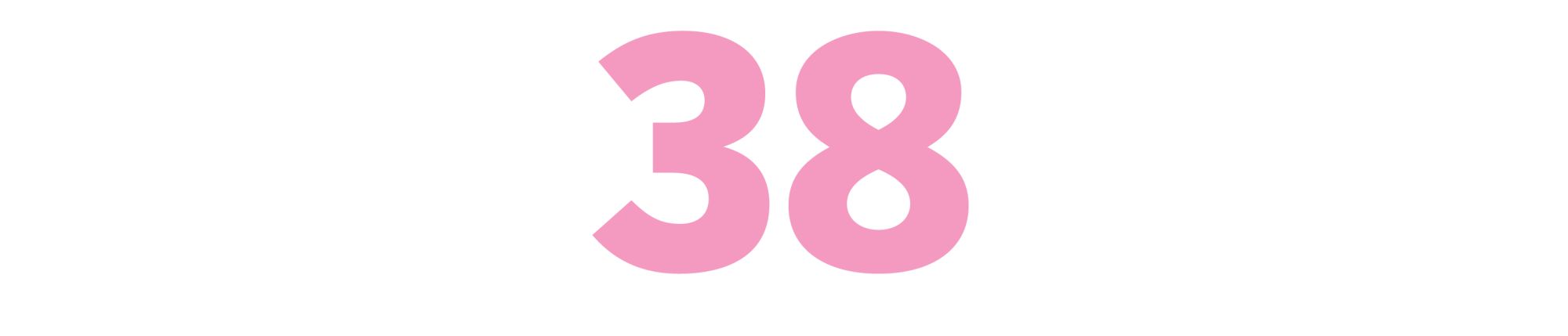
Madly, Deeply: The Diaries of Alan Rickman
(Alan Rickman, 2022)

Today, the late British actor might best be known for playing stern wizard Severus Snape in the “Harry Potter” film franchise. But in a career spanning nearly four decades, he amassed a wide-ranging collection of on-screen personas. What these diaries reveal, however, is that perhaps the Rickman behind the scenes was the most compelling character. The compilation of forthright entries opens a window into his most intimate moments with friends and loved ones, as well as memorable professional experiences. The self-portrait that text pieces together is that of a multifaceted person and artist with a singular perspective on his craft and on quotidian life. — CA

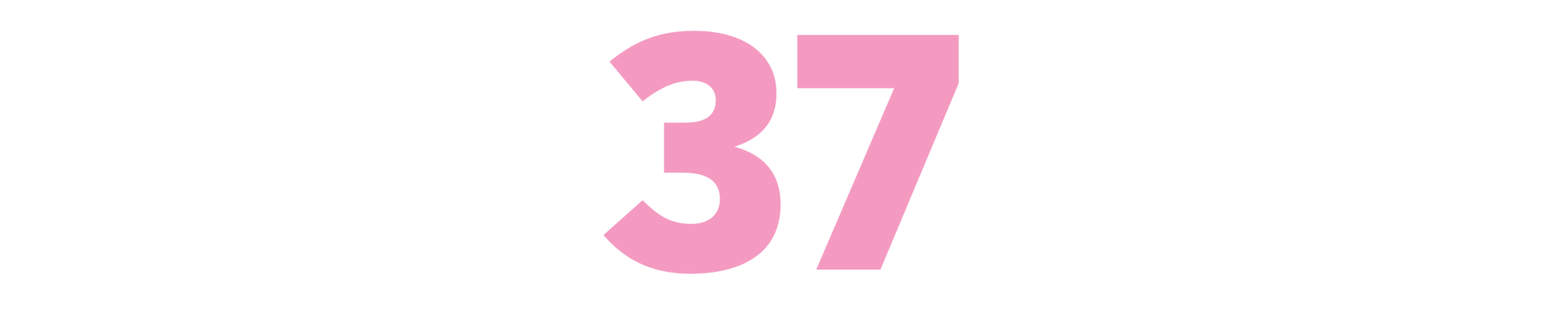
Monsters: A Fan’s Dilemma
(Claire Dederer, 2023)

Perhaps the most exhilarating thing about this book is not the subject matter — can we consume art after learning how monstrous the artist is? — but how Dederer puts her thinking about it down on the page. She considers all the angles on Roman Polanski, the film director who pleaded guilty to having sex with a minor in 1977 and has been accused of other incidents of sexual assault — who also himself suffered extraordinary trauma and has (significantly to Dederer, once a film critic) made great movies. She is more forgiving than you might think, which allows her fascinating book to invite engagement. In addition to filmmakers, she looks at writers, musicians and actors and also female monsters (bad mothers). Winner of the L.A. Times’ 2023 Christopher Isherwood Prize for Autobiographical Prose, this book is a remarkable artistic inquiry. — CK

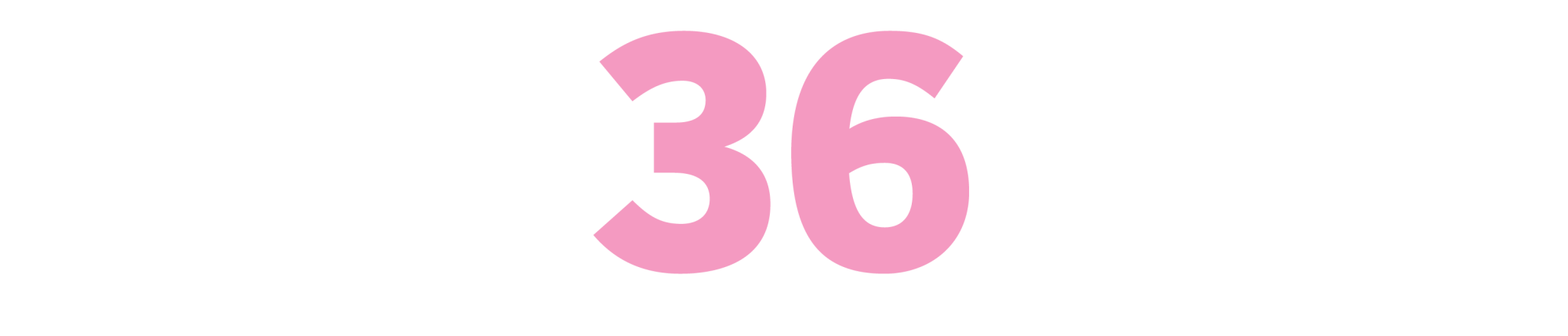
Memo From David O. Selznick
(David O. Selznick, selected and edited by Rudy Behlmer, 1972)

If you want to learn about how to produce, this is an incredibly fun way to do it.
— DAVID MADDEN, head of global entertainment for Wattpad WEBTOON Studios and former executive at Fox, AMC Networks and Berlanti Television

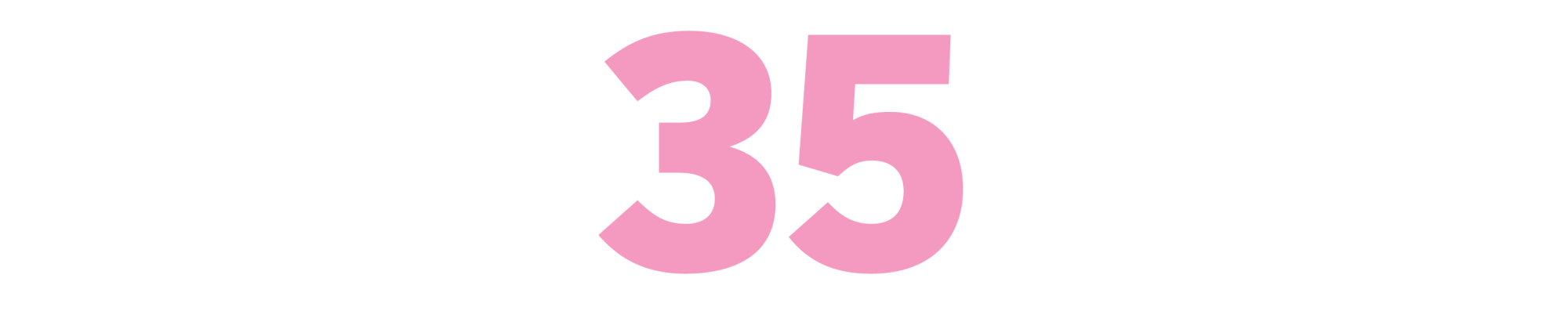
Valley of the Dolls
(Jacqueline Susann, 1966)

Susann was no great shakes as a model and actor. But when she turned to a typewriter, the entertainment world quivered. “Valley of the Dolls” hit Hollywood like a mile-wide powder puff — everyone paged through her bestseller looking for fingerprints. Could its ruthless and needy singer Neely O’Hara be inspired by Judy Garland? Was Jennifer, the doomed blond, based on Carole Landis or Marilyn Monroe? Was anyone in the industry sober? Like the characters she channeled, Susann was a pill-popper roiling with frustrated ambition, a never-was starlet who’d been close enough to the action to hear the good gossip. (The novel’s interconnected affairs remind us that show business was, and is, a very small clique.) Her witty and tireless self-promotion became the modern template of a celebrity author. Responding to rumors that the book’s tyrannical Broadway star was based on her former friend Ethel Merman, Susann quipped, “We didn’t speak before the book came out. Let’s just say that now we’re not speaking louder.” — Amy Nicholson

From Reverence to Rape: The Treatment of Women in the Movies
(Molly Haskell, 1974)

At the time of its publication, Haskell writes in her introduction to the third edition of “From Reverence to Rape,” she “wanted to show how women had in fact been better served by the notoriously tyrannical studio system than they were in the newer, freer, hipper Hollywood of the (then) present. This has since become a truism, but in 1974 it was heresy.” More than any single point she draws about women’s place in the American cinema, though, whether via her discussion of “the woman’s film,” her decade-by-decade history or her comparison to European patterns, it’s Haskell’s refusal to hew to received wisdom that has sustained the book’s relevance for 50 years. Evincing no patience for pat readings or political agendas, Haskell effortlessly underscores the notion that the meaning of movies can’t be plotted on a chart, and no matter where the critical consensus at a given moment lies, her chewing over films from “His Girl Friday” to “Carnal Knowledge” — whether they go down easy or get stuck in her craw — remains timeless. — Brennan

Hollywood Babylon
(Kenneth Anger, 1965)

Given the number of inaccuracies, falsehoods and all around debunked stories found in “Hollywood Babylon,” you’d be forgiven for thinking this salacious collection of scandals has no merit. Then again, the brainchild of one of the most avant-garde queer filmmakers of the 20th century is less interested in facts about show business than in revealing the lurid underbelly that’s long cemented it. Originally published in France in 1959, the book first arrived in the U.S. in 1965, but it was the image-heavy edition printed a decade later that ignited the controversy that follows it to this day. Riddled with off-color anecdotes tackling everything from incest to suicide and featuring marquee stars from the ’20s and ’30s including Fatty Arbuckle, Lupe Velez and Clara Bow, it more than lives up to how the New York Times described it: a “306‐page box of poisoned bonbons.” — Betancourt

The Jaws Log
(Carl Gottlieb, 1975)

Gottlieb witnessed firsthand the complications that surfaced during the production of “Jaws,” the first summer blockbuster. A friend of the young Steven Spielberg, who was only 28 when he directed the imposing shark story based on Peter Benchley’s novel, Gottlieb first came on board to act in a small role and to work on improving the screenplay. But he ultimately chronicled the young director’s feat as it was unfolding. The meticulously told account provides insight into the problem-solving approach of Spielberg and his collaborators when faced with a myriad of crises. In doing so, the journal illustrates the titanic collective effort making a movie entails and the uncertainty about how the end result will turn out, even when you have the future wunderkind of cinema at the helm. — CA


You’ll Never Eat Lunch in This Town Again
(Julia Phillips, 1991)

To see Julia Phillips become the first female producer to win a best picture Oscar is to get a glimpse of the charisma and wit that made her so welcome in Hollywood, in boardrooms and on sets, until she wasn’t. At the 1974 Academy Awards, a streaker had interrupted David Niven introducing presenter Elizabeth Taylor, who stumbled over her lines, then announced “The Sting” as the winner. Phillips took the stage with her (not yet ex-) husband, Michael, and their co-producer Tony Bill. Phillips, with a touch of New York accent, said, “You can imagine what a trip this is for a Jewish girl from Great Neck. Tonight I get to win an Academy Award and meet Elizabeth Taylor all in the same moment.” Off-screen, Taylor guffaws. > GO TO STORY

L.A. Confidential
(James Ellroy, 1990)

Ellroy’s cynical noir takes such a dark view of Los Angeles that the city is practically a black hole. The gravitational force is, of course, Hollywood and its insatiable need for sex, drugs, money and power (and criminals willing to supply them). Ellroy named names — Mickey Cohen, Johnny Stompanato — and barely disguised others, such as his entertainment tycoon Raymond Dieterling, who wants to build a theme park for his character Moochie Mouse. Most damningly, though, Ellroy describes a Los Angeles Police Department that functions like a movie studio. Here, every officer’s career hinges on their ability to put on a performance. The cops script phony hearings, stash props on perps, rehearse their threatening zingers, stage massacres that make them look like heroes and dress up for flashy narcotics busts in blue blazers that bring out their eyes. To Ellroy, the LAPD doesn’t want to protect and serve — it just wants applause. — AN

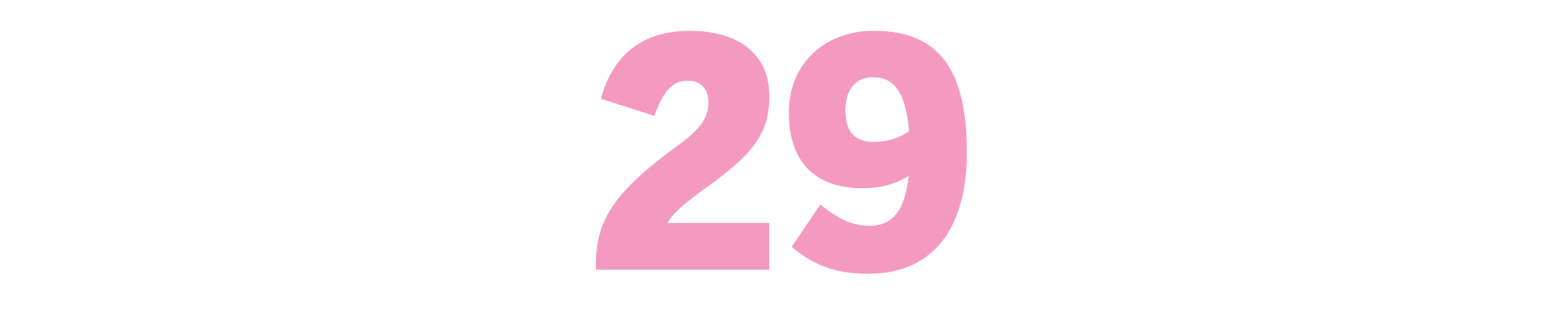
The Celluloid Closet: Homosexuality in the Movies
(Vito Russo, 1981)

First published in 1981, “The Celluloid Closet” was the culmination of decades’ worth of work by film historian and LGBTQ activist Russo. Initially designed as a live lecture with clips from classic films that showed queer-coded characters, cruel homophobic stereotypes and everything in between, Russo’s ambitious tome chronicled the many ways Hollywood had depicted gays and lesbians on the big screen. With sections such as “Who’s a Sissy? Homosexuality According to Tinseltown” and “Struggle: Fear and Loathing in Gay Hollywood,” Russo’s encyclopedic study was a groundbreaking intervention into discussions of visibility and representation that are nowadays shepherded by the likes of GLAAD, the very organization Russo founded. The influential nonfiction book would go on to be reissued in 1987 with more contemporary additions and in 1996 was adapted into a Peabody Award-winning documentary by the same name, narrated by Lily Tomlin. — Betancourt

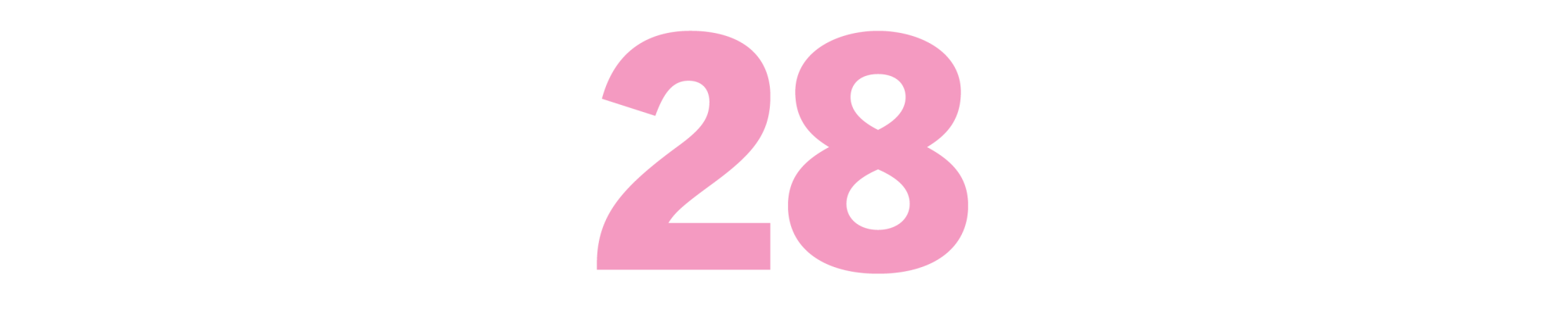
Lulu in Hollywood
(Louise Brooks, 1982)

Brooks was best known for G.W. Pabst’s 1929 drama “Pandora’s Box,” in which her Lulu, a ferocious flapper with a pageboy haircut, seduced and abandoned all men who dared stand in her path. But she was also an astute observer of show business customs and personalities, and, as it turned out, a very good writer. This collection of personal essays covers subjects ranging from her time working with director William “Wild Bill” Wellman on “Beggars of Life” to her friendship with Humphrey Bogart, of whom she writes: “Humphrey Bogart spent the last twenty-one years of his life laboriously converting the established character of a middle-aged man from that of a conventional, well-bred theater actor named Humphrey to one that complemented his film roles — a rebellious tough known as Bogey.” Brooks was very wise to the ways of image; she also deftly transcended her own. — CV

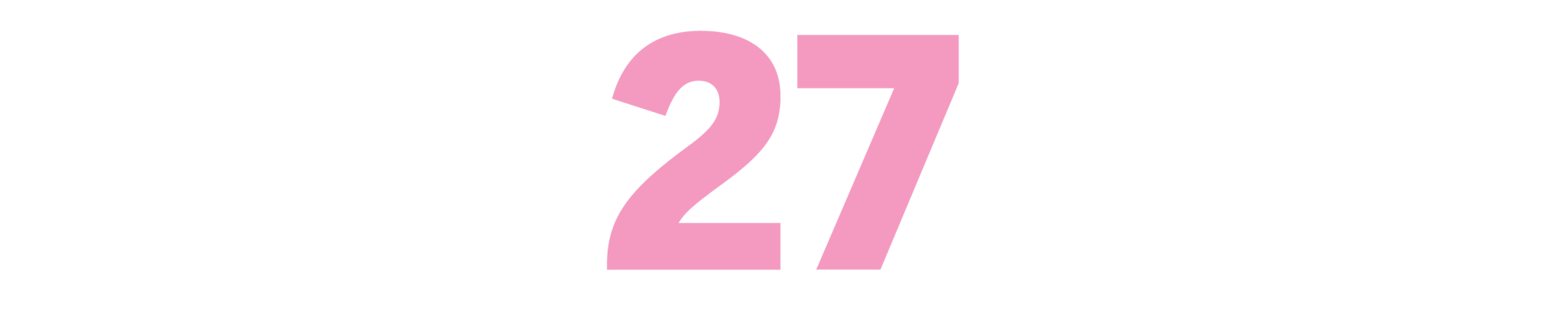
The Conversations: Walter Murch and the Art of Editing Film
(Michael Ondaatje, 2002)

One of the editors on bona fide classics such as Francis Ford Coppola’s “Apocalypse Now” and “The Conversation,” three-time Oscar-winner Murch holds a well of hard-earned knowledge about the mechanics of visual storytelling. A portion of that narrative wisdom is contained within the pages of this collection of rich exchanges with lauded novelist Ondaatje. (The pair met during the making of Anthony Minghella’s “The English Patient,” a film adapted from Ondaatje’s book and edited by Murch.) The intellectual wealth of these chats goes beyond film editing — an often-misunderstood craft that is absolutely essential to how we perceive cinema — and extends to the overall history of the medium in the last third of the 20th century. — CA

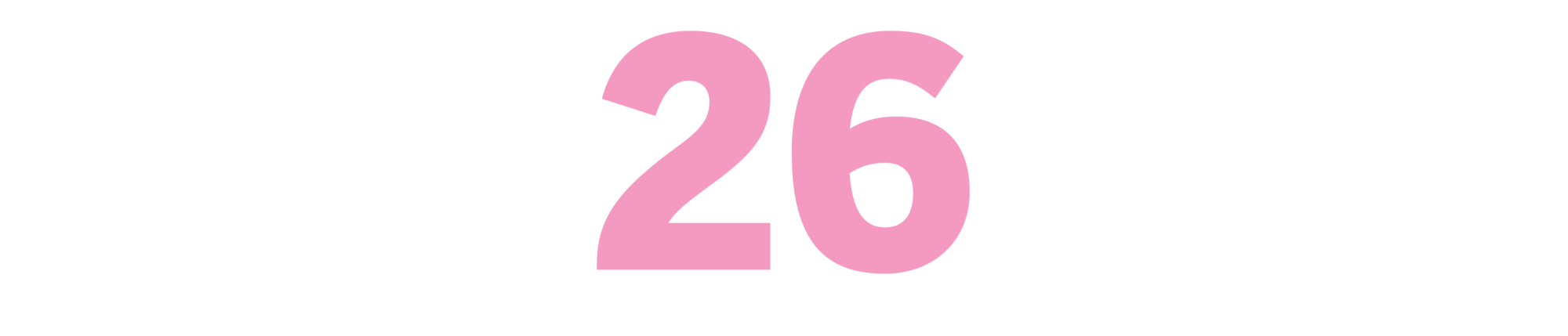
Money: A Suicide Note
(Martin Amis, 1984)

In the late 1970s, Amis wrote the screenplay for an unremarkable science-fiction film, “Saturn 3.” On the evidence of this savage industry satire, the experience was souring, dehumanizing and debauching. John Self, the novel’s narrator, is a hard-drinking director traveling between New York and London to steer a film titled “Good Money,” and his observations are rich with fine-grain detail about the celebrities and agents essential to the movie business. But it’s as much a story about the movie business’ relentless damage to the psyche, as John is sunk in porn and prostitutes and drink, swallowed up not just by his success but his lust for it. “The artists in my story are bull artists, con artists, drink artists,” Amis told an interviewer about “Money.” But not good artists, morally or cinematically. — MA

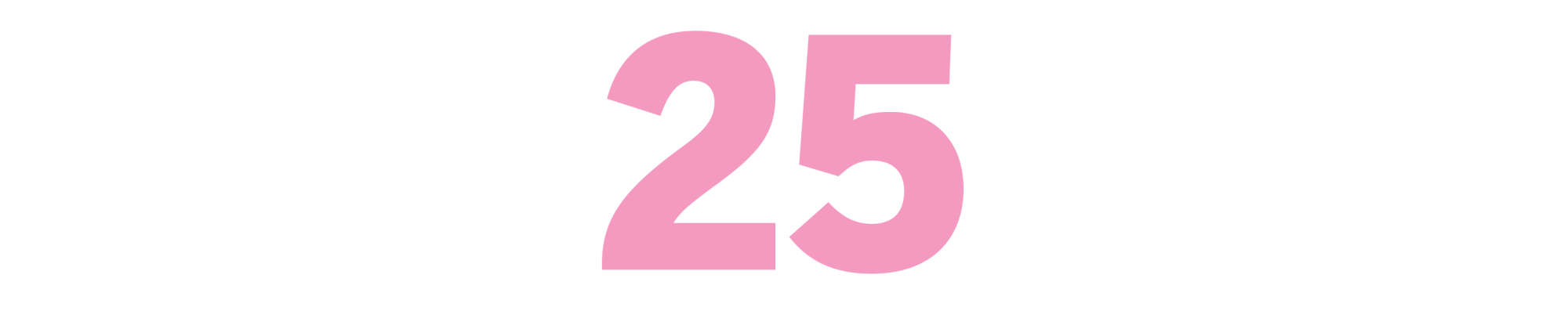
Third Girl From the Left
(Martha Southgate, 2005)

Hollywood always seemed a mythical place where average folks could make the wildest of their dreams come true. But once you’ve been around a while, you come to see the tarnish on Tinseltown’s tinsel. The Black women in “Third Girl From the Left” want to be movie stars or movie makers, but they arrive in a Hollywood that’s not ready to love them back. A family story that gets its shine from the lure of movie magic and our shared fantasy about the healing powers of stardom, Southgate’s novel never shies away from the hard truths of dream-chasing, yet still believes “in the power of movies and the people in them to change a life.”
— LAURA WARRELL, author of “Sweet, Soft, Plenty Rhythm”


Beautiful Ruins
(Jess Walter, 2012)

“I’ve been simultaneously drawn to and repelled from Hollywood for years,” Walter told The Times in 2012. Both sentiments feed into this novel, which begins when a beautiful actor, banished from the set of “Cleopatra” where Elizabeth Taylor and Richard Burton are indulging in gorgeous excess, lands at a small hotel on the Italian coast. The hotelier is smitten. Jump ahead five decades to reality television in Hollywood, where the assistant to an on-his-way-down producer has to listen to terrible pitches. The novel jumps around temporally and includes an unfinished manuscript and an awful memoir, but these disparate threads tie together in a delightful resolution. “Hollywood is like a giant mirror, I think,” Walter said, “and I used it that way in the book, reflecting characters back to themselves.” — CK

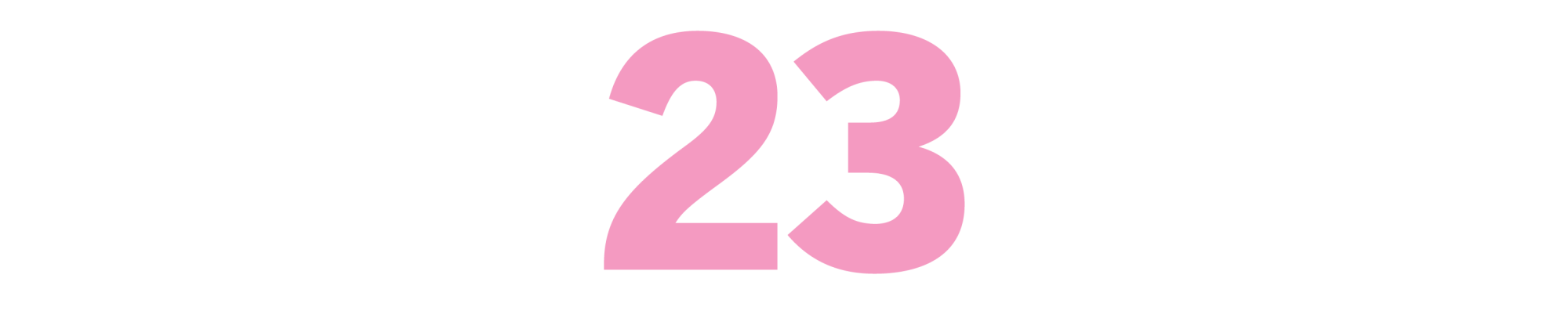
Eve’s Hollywood
(Eve Babitz, 1974)

Few have loved this city as ferociously as Babitz, a brilliant chronicler of Hollywood’s fantasies, foibles and beautiful freaks. Babitz, who died in 2021, grew up here knowing everyone. Her godfather was famed composer Igor Stravinsky; her high-school gym locker was next to that of a girl who later joined the Manson Family. Babitz’s gleefully debaucherous memoir captures her teen years as a glamour-mad adventuress pinballing around a town full of kooks. At once skeptical and star-struck, she writes passionately about celebrity, superficiality and excess and justifies her decision to graduate early in just two words: Marlon Brando. Celebrities adored Babitz right back, but luckily for us, she chose to be an author, not an actor. “I never had the necessary ability to suspend my own disbelief,” she shrugs. Besides, Babitz knew the juiciest drama plays out off-screen. — AN


The Big Sleep
(Raymond Chandler, 1939)

To Chandler, one of the godfathers of the hard-boiled crime novel, Hollywood generally came down to blackmail and sleaze. (To be fair, to Chandler, much of the world came down to blackmail and sleaze). “The Big Sleep,” the first of Chandler’s seven Philip Marlowe novels, finds the private dick investigating a pornography ring in a story that finds murders and double-crosses piling up at a dizzying rate. An honorable old man hires Marlowe to extricate his younger daughter from a series of blackmailers; meanwhile, the detective falls for his client’s older daughter. Gleefully homophobic and brutal, adapted into an indelible 1946 Howard Hawks movie starring Humphrey Bogart and Lauren Bacall, the novel set the stage for “The Little Sister” (1949), in which Marlowe investigates a blackmail scheme targeting a Hollywood starlet. By then Chandler had done time as a screenwriter and didn’t care for the industry; he got his revenge on the page. — CV


West of Eden: An American Place
(Jean Stein, 2016)

The title of Stein’s oral history of the muddled, murky origins of Los Angeles as we know it gestures at an off-kilter narrative of biblical proportions. Here is Hollywood laid bare as a fabled “American Place” that’s not so much an Edenic garden as something darker and dirtier, though not for that any less sinful. Stein focuses on families and individuals who forged this West Coast city into what it is today. Oil tycoon Edward L. Doheny, movie mogul Jack Warner, actor Jennifer Jones, heiress Jane Garland and MCA founder Jules C. Stein (the author’s father) anchor startling as-told tales about a city built on ruthless individuals whose bloodied legacies live on still. The Times best summed up its appeal: “It’s like being at an insider’s cocktail party where the most delicious gossip about the rich and powerful is being dished by smart people.” — Betancourt

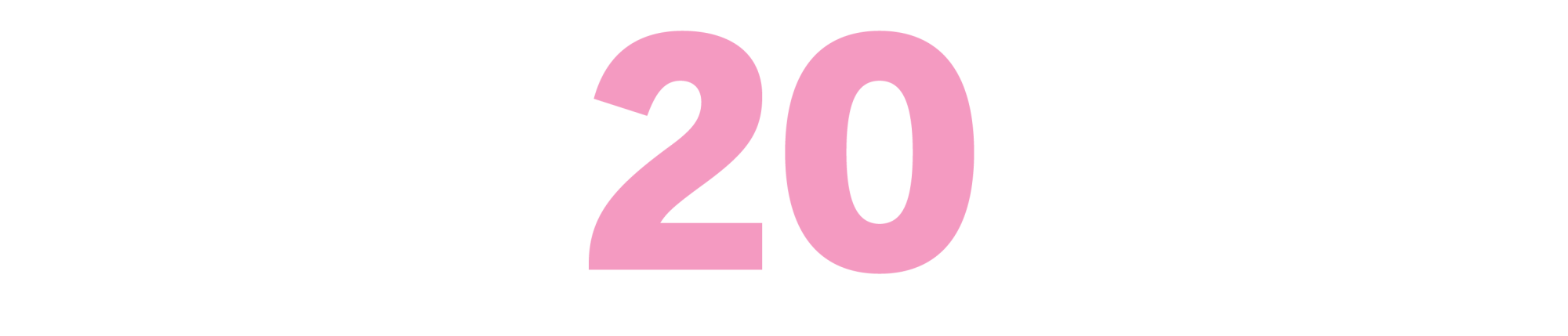
Erasure
(Percival Everett, 2001)

“When I grew up, there were three black people on TV, and they were all porters,” author Everett once groaned. His exasperation with stereotypes fuels this flashpoint novel about a Black academic named Monk who invents an ex-felon persona to sell books. “Erasure” is aimed at literary gatekeepers, but Everett takes a shot at Hollywood, too, with his inclusion of a bearish, cigar-smoking movie producer who barges into the story alongside a giggling silicone blond. (The bore jokes that he should have met Monk at Popeye’s Fried Chicken.) When filmmaker Cord Jefferson reworked “Erasure” into his Oscar-winning screenplay, “American Fiction,” he updated the producer character into a vapid dweeb who thinks he’s speaking woke. The tweak emphasized the baby steps the industry has made since 2001 — and the miles left to go. Now who’s going to film “James,” Everett’s bold new adaptation of “Huckleberry Finn”? — AN

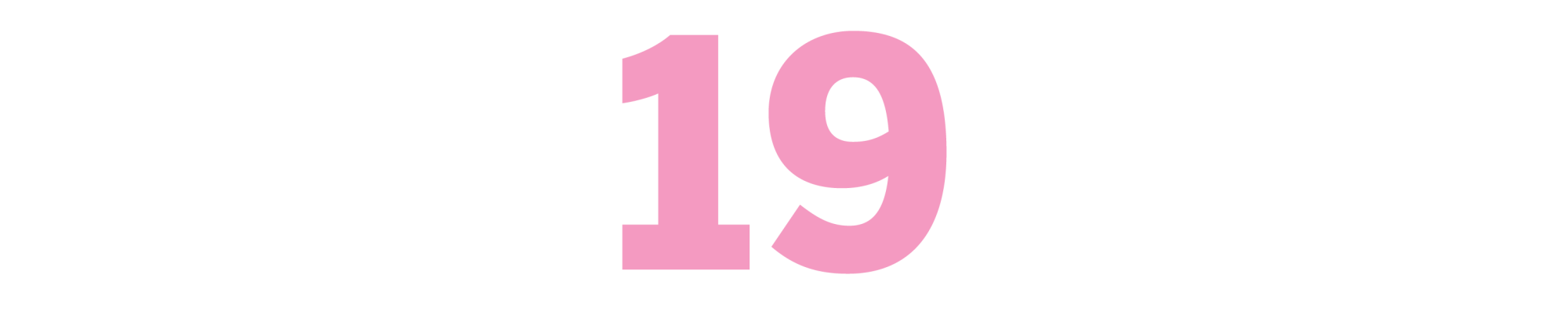
The Studio
(John Gregory Dunne, 1969)

Dunne was dumbfounded when Twentieth Century Fox head Richard Zanuck gave him full access to cover the studio over the course of a year that included production of movies including “Dr. Dolittle,” “Planet of the Apes” and “The Boston Strangler.” But he knew just what to do with the gift. Sitting in on marketing and production meetings, hanging out in the commissary, watching dailies, Dunne captured the small moments that add up to a big picture of ego run amok in a sort of hinge era for the industry, when audiences were getting younger and edgier and studios still weren’t sure how to respond (see “Dr. Dolittle.” Or better yet, don’t). Here’s Zanuck, watching “Apes” footage, responding to criticism in the room that a blood transfusion is depicted incorrectly: “What the hell. Maybe that’s how an ape does it.” Indeed. As Dunne writes in his foreword, “If I got the access, I knew I had the book.” — CV


Final Cut: Art, Money and Ego in the Making of Heaven’s Gate, the Film That Sunk United Artists
(Steven Bach, 1985)

When Steven Bach’s “Final Cut” appeared in 1985, it was mainly sold as Hollywood dish. Bach, the former head of production at United Artists, had delivered the inside story of “Heaven’s Gate,” a 1980 epic western by Michael Cimino that was budgeted at about $11.5 million, wound up costing around four times that, and prompted the hobbled studio’s sale to MGM. Here at last were the details of Cimino’s outsize ego and UA’s futile attempts to restrain it. > GO TO STORY

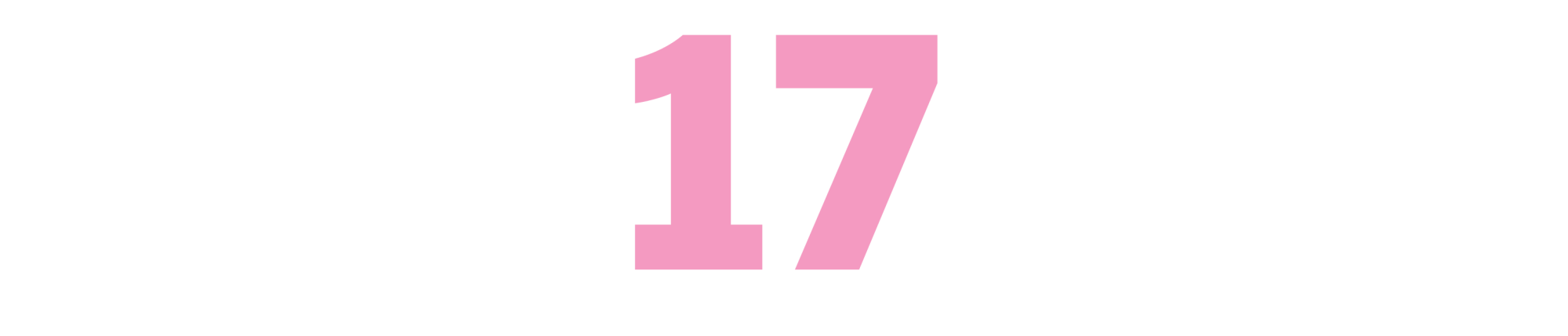
The Classical Hollywood Cinema: Film Style and Mode of Production to 1960
(David Bordwell, Janet Staiger and Kristin Thompson, 1985)

When renowned scholar Bordwell died earlier this year at 76, current and former film students the world over shared images of his introductory textbook “Film Art,” whose changing cover illustration helped distinguish one generation of cinephiles from another as surely as the release of “The Graduate” or “sex, lies, and videotape.” But for my money, his most indispensable contribution to our understanding of the medium, co-written with Thompson and Staiger, is this magisterial survey, illustrated with frames from “King Kong” (1933), “The Magnificent Ambersons” (1942) and “Carmen Jones” (1954), among countless others. In it, the authors not only explain the rise of the studio system, trace the emergence of sound and color, and explore the evolution of film exhibition from cramped nickelodeons to imposing movie palaces. They also argue, convincingly and definitively, that the political economy of Hollywood moviemaking is inextricable from the style and content of Hollywood movies — and thereby reveal the scaffolding underneath the greatest meeting of art and business the world has ever known. — Brennan

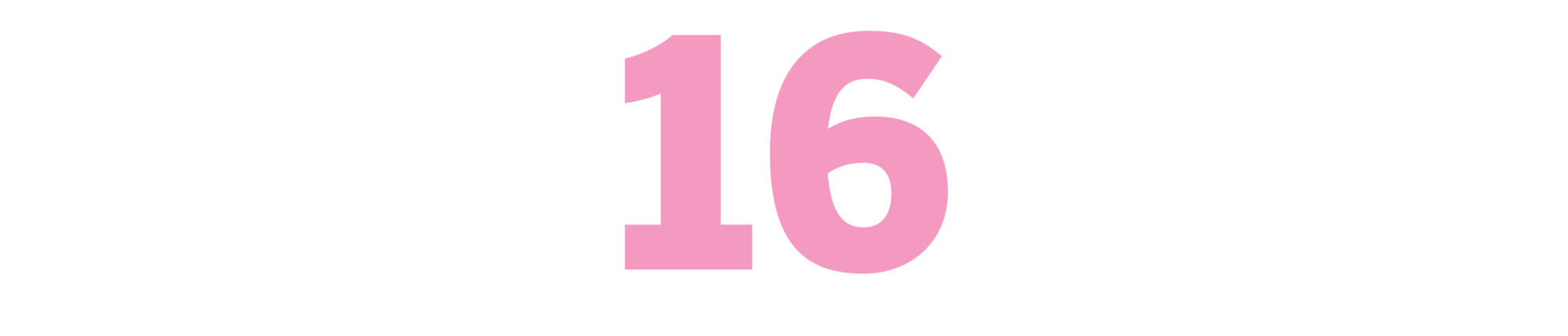
The Devil’s Candy
(Julie Salamon, 1991)

First subtitled “The Bonfire of the Vanities Goes to Hollywood,” this book is an inside look at the making of a single film, based on Tom Wolfe’s bestselling novel. The step-by-step chronicle, however, has proved more enduring than the original text; later editions are subtitled “The Anatomy of a Hollywood Fiasco.” Salamon, a Wall Street Journal film critic, had been looking for a director who would allow her full access to the making of a film, and Brian De Palma suggested “Bonfire,” no constraints. She gets a kaleidoscopic view of the filmmaking process, speaking to the second-unit director, editor, producers, stars, people standing on set. Nobody wanted to make a flop. But what started out as a satire of ’80s greed and extravagance, with a budget that swelled to nearly $50 million, became a cautionary tale instead. Salamon’s narrative is clear-eyed and delicious. — CK


Postcards From the Edge
(Carrie Fisher, 1987)

“Maybe I shouldn’t have given the guy who pumped my stomach my phone number, but who cares?” There is no more quotable novel about Hollywood than Carrie Fisher’s roman à clef, “Postcards From the Edge.” Fisher’s sentences bristle with caustic, self-effacing humor. Outside of her forays into that galaxy far, far away, that brand of sharp deadpan comedy is perhaps what the former Princess Leia would become best known for. And in her debut novel, the actress-turned-writer makes great use of her enviable way with words. > GO TO STORY

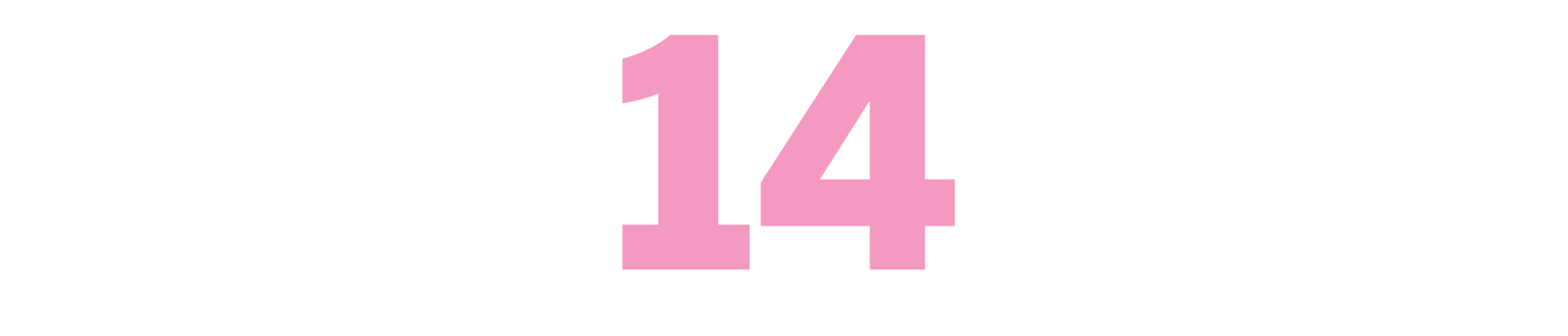
What Makes Sammy Run?
(Budd Schulberg, 1941)

Much of the Hollywood that Schulberg imagined in this 1941 classic doesn’t exist anymore — gone are the studio structure and the contract screenwriters, not to mention much of the casual bigotry. But amoral striving? Talentless hacks somehow reaching the top of the heap? That stuff is deathless, and in Sammy Glick, Schulberg invented one of the most enduring craven strivers in American literature. Starting as a copy boy at a New York paper, Glick connives, plagiarizes, seduces and schemes his way into Hollywood from writer to producer to studio head. (That’s not a spoiler: It’s clear from the start that Schulberg will have his antihero fail upward to extremes.) The book is narrated by Al, a humbler colleague bemusedly observing Glick’s rise, and the frisson between the two underscores the inherent tension in moviemaking: How cruel people can be for the sake of making something that captures our hearts. — MA

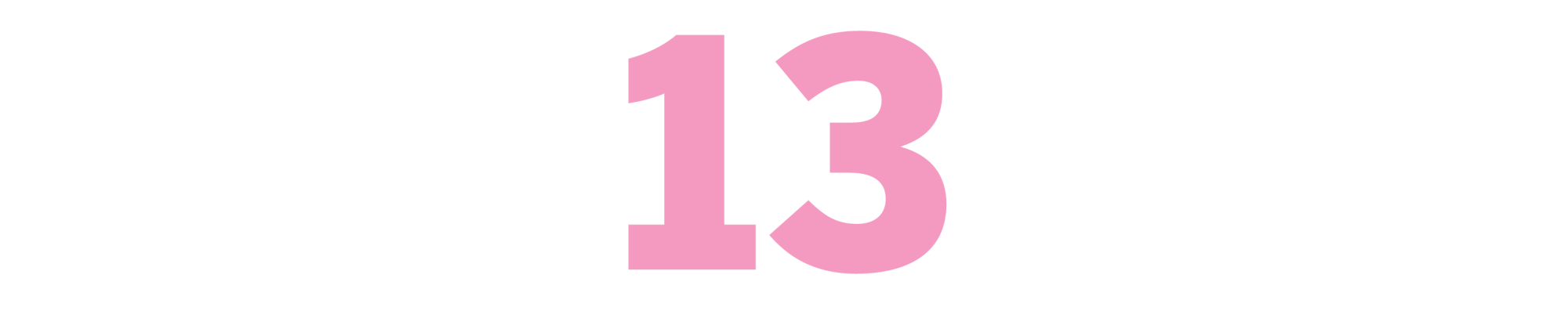
The Kid Stays in the Picture
(Robert Evans, 1994)

When Evans’ autobiography was adapted into a film in 2002, the cover for the book’s movie tie-in edition advertised what had drawn readers to this Hollywood tell-all: “Success. Scandal. Sex. Tragedy. Infamy,” its cover read. “And that’s just the first chapter …” Such a titillating promise was warranted. Evans’ life and career was rife with the kind of juicy anecdotes that make such memoirs endlessly enjoyable reads, and his is unparalleled in that regard. It tracks his rise from radio star hand-plucked into movie screen stardom by Norma Shearer through his later days running Paramount Pictures, shepherding the studio through pics such as “The Odd Couple,” “Rosemary’s Baby” and “The Godfather.” But Evans’ natural raconteur instincts are even better suited to depicting his cocaine benders, explaining his implication in “The Cotton Club Murders” case and detailing how he found his way back on top in a town that loves a good comeback story. — Betancourt

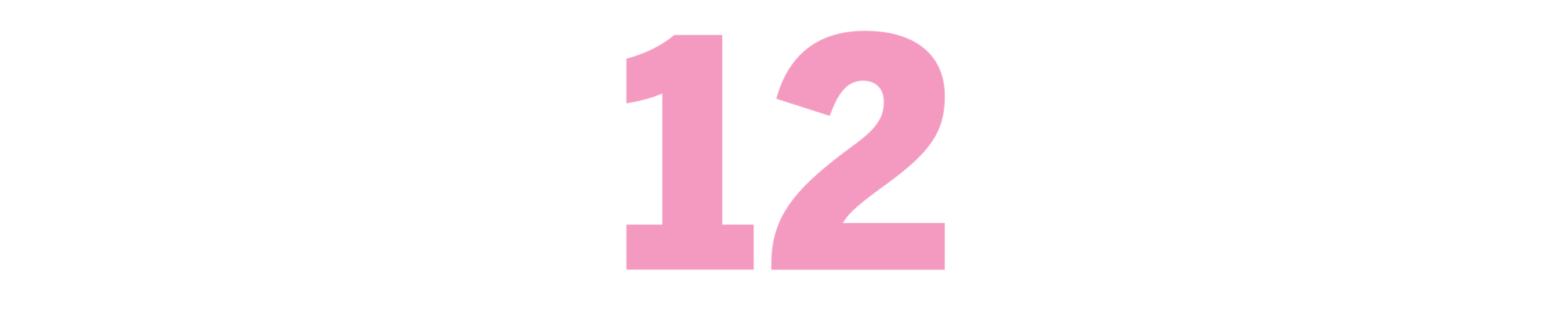
The Pat Hobby Stories
(F. Scott Fitzgerald, 1940-41)

These 17 short stories, originally published by Esquire and later collected in a 1962 book, chronicle the misadventures of a failing, flailing screenwriter, a role that Fitzgerald, whose downward spiral accelerated when he went west to write for the pictures, knew all too well. Vain, often drunk, desperate to get a leg up, the title character weaves in and out of humiliating scenarios, scraping by with a sense of self-inflation to match his appetite for self-destruction. “The Last Tycoon,” Fitzgerald’s unfinished novel based on the life of producer Irving Thalberg, was the author’s Hollywood tragedy; the Hobby stories are the comedy, and they remain side-splittingly funny. As a screenwriter, Hobby was once heralded as “a good man for structure,” which seems appropriate; these stories bend in all the right places. To modern eyes, in their depiction of zigzagging pettiness, they feel like progenitors of “Curb Your Enthusiasm.” Fitzgerald died of a heart attack in 1940, before the last of the Hobby stories were published. — CV

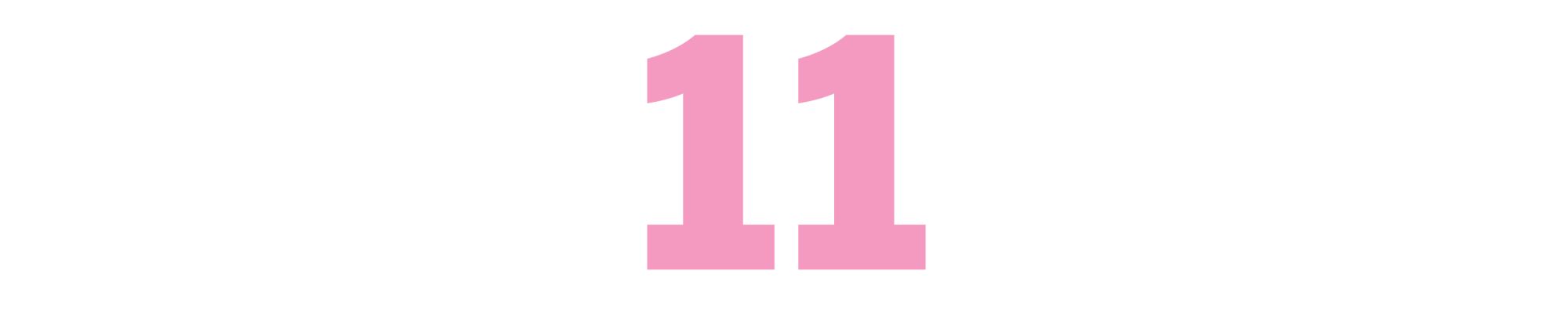
Five Came Back: A Story of Hollywood and the Second World War
(Mark Harris, 2014)

None of Harris’ three books would be out of place on this list. “Pictures at a Revolution” is a fascinating portrait of the highs and lows of an industry in tumult, and “Mike Nichols: A Life” is an unputdownable biography of one of modern Hollywood’s most perceptive filmmakers. But it’s to “Five Came Back” that I continue to turn in something like awe: Across five filmmakers and nearly a decade, through archival research and careful criticism, the author manages to construct an accessible yet never-less-than-rigorous history of Hollywood at war — a subject that has not received the same attention in mainstream film writing as the Hollywood Renaissance or the rise of the franchise blockbuster. Perhaps most thrilling, Harris’ approach allows us to see the effect John Ford, George Stevens, John Huston, William Wyler and Frank Capra had on the American war effort as well as the effect it had on them. You’ll never look at any of their filmographies the same way again. — Brennan

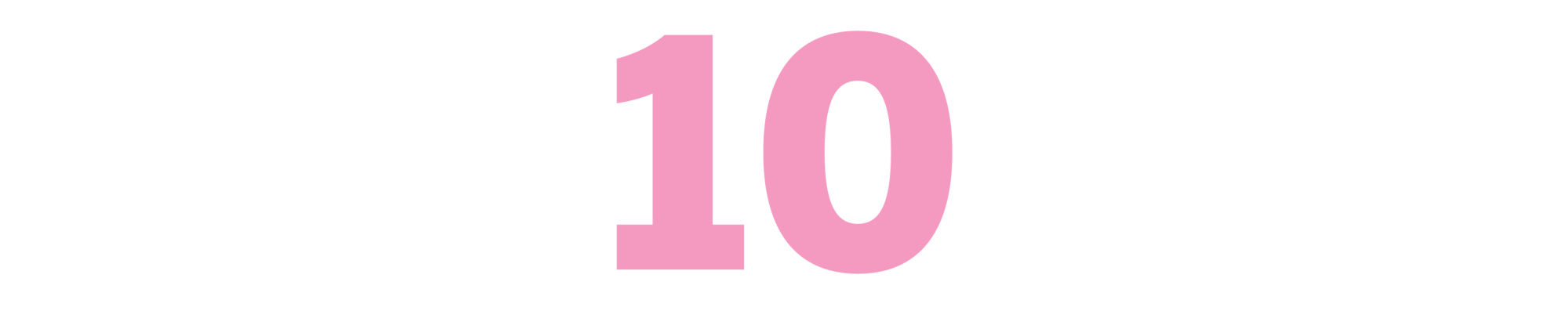
Making Movies
(Sidney Lumet, 1995)

Wise, plainspoken and infused with disarming humility, the late Lumet’s book is like a master class with a teacher you want to hang out with all the time. “We really do know what we’re doing,” he writes. “It only looks like we don’t.” Lumet certainly did, and with directorial credits including “12 Angry Men,” “Dog Day Afternoon” and “Network,” he made it look easy. Guiding the reader through the various elements of filmmaking, from writing and shooting to acting and editing, Lumet is far more compassionate than vindictive. “They’re annoying, publicists, but their lives are hell.” “I love actors. I love them because they’re brave.” But this is no catalog of platitudes. “Making Movies” is stocked with usable advice and examples, the time he didn’t think Paul Newman was quite drilling into his character in “The Verdict,” sent him home for the weekend and got the Newman magic on Monday. “Paul is a shy man,” Lumet writes. “And a wonderful actor. And a race car driver. And gorgeous.” — CV


Easy Riders, Raging Bulls: How the Sex-Drugs-and Rock ‘n’ Roll Generation Saved Hollywood
(Peter Biskind, 1998)

Reassuringly, the two golden ages of American film each arrived in the wake of utter chaos. The roughly simultaneous advent of talking pictures and the Great Depression ushered in the glories of the 1930s; decades later, the collapse of both the Hollywood studio system and American optimism in Vietnam helped soften the ground for such 1970s classics as “Chinatown,” “The Godfather Part II” and “The Conversation.” > GO TO STORY

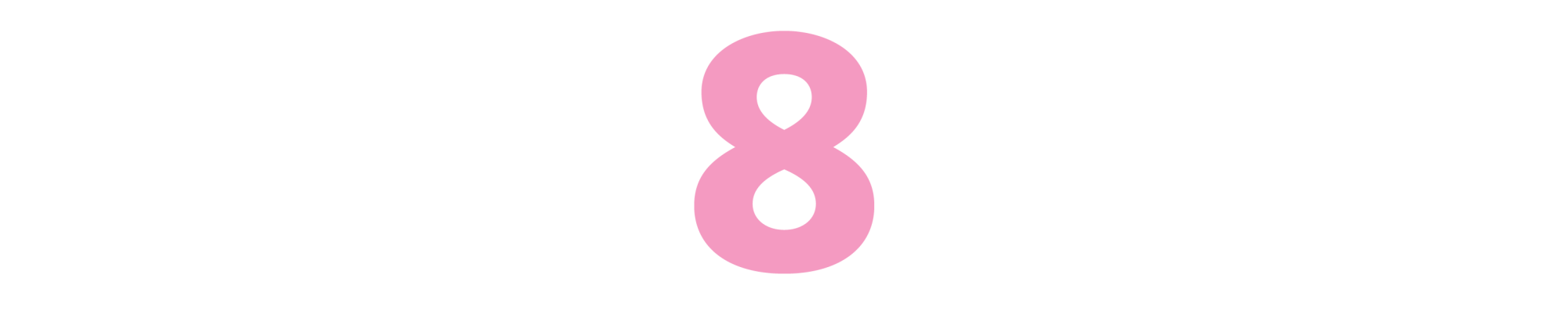
Interior Chinatown
(Charles Yu, 2020)

Starring Generic Asian Man: The background players take central stage in this hilarious Hollywood novel, winner of the 2020 National Book Award. Our hero, often seen on the edges of a “Law & Order”-type television show, wants more. He lives in a crummy apartment building above a Chinese restaurant, where people from across Asia get lumped together, their individuality shown to us but not the world. Informed by his experience as a second-generation Taiwanese American, Yu skewers shallow racism and toys with cultural tropes. Told in the form of a screenplay — Yu was a writer on “Westworld” — “Interior Chinatown” is a love story, a coming-of-age story, a satire and literary accomplishment. The phrase “Interior Chinatown” is, yes, screenplay shorthand for a scene’s setting, but it also reflects the interior narrative only a novel can explore. — CK

Picture
(Lillian Ross, 1952)

The book is usually better than the movie. That’s certainly the case with Stephen Crane’s hallucinatory 1895 Civil War novel, “The Red Badge of Courage,” the source of a 1951 film version that flopped thanks in part to studio meddling. But sometimes the book about the adaptation is better than either. Ross’ 1952 book on the making of “Badge,” originally written for the New Yorker, is a classic of fly-on-the-wall reportage, following director John Huston, MGM studio heads and the film’s cast and crew from conception to shooting to post-release excuse-making. Ross can be meticulous almost to the point of fustiness; she seemingly got hold of every internal memo and expense sheet. But there are few better books about the soup-to-nuts creation of a film, and it’s a brilliant profile of Huston, who’s trying to both gladhand the execs and keep them at arm’s length. — MA

The Player
(Michael Tolkin, 1988)

A postcard arrives at Griffin Mill’s office one day: “You said you’d get back to me. I’m still waiting.” The young Hollywood exec, ambitious to a fault as he climbs his way to the top, wavers over telling anyone about what soon becomes a series of death threats from, of all things, an aggrieved writer. Making savvy use of that thriller conceit, Tolkin’s wildly entertaining first novel offers a front-row seat to the self-absorption that characterizes those who would (and do) become mythmakers in Tinseltown. As Mill goes to increasingly deranged lengths to identify who is behind those ominous missives — all while making sure his position at the studio isn’t eclipsed by any newcomers, power lunches taking precedence over anything else — Tolkin paints a scathing portrait of a city of dealers and players who’d do anything to win. Yes, even murder. — MB

Adventures in the Screen Trade
(William Goldman, 1983)

Best remembered now for “The Princess Bride” — he wrote both the novel and the screenplay — Goldman was previously best known for his Oscar-winning screenplay for “All the President’s Men,” the indelible story of two journalists chasing the truth behind Watergate. Before that, though, he was the guy who created “Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid,” a box-office smash, a buddy film western with an entirely unexpected ending. How on earth did the same person write all those classic films and more (“Misery,” “Harper,” “Marathon Man”)? Imagine sitting down at a bar next to him and getting a chance to ask. This book is that conversational — chatty, filled with vivid anecdotes, revealing industry secrets. Part self-effacing memoir, part how-to for writing screenplays, and a window into how the levers of power worked in Hollywood, this book is a stone-cold classic. — CK

Get Shorty
(Elmore Leonard, 1990)

Suave loan shark Ernesto “Chili” Palmer is our guide through this amusing crime saga set in the underbelly of the seemingly glamorous world of Hollywood moviemaking. Tasked with collecting the cash that Los Angeles-based producer Harry Zimm owes a Las Vegas casino, Chili quickly becomes entangled in backdoor deals to finance prospective film productions. As increasingly dangerous parties become tangentially involved, Chili and Zimm risk losing more than just their big-screen aspirations. Barry Sonnenfeld’s 1995 big-screen adaptation of the tome starred John Travolta, Gene Hackman, Rene Russo and Danny DeVito and became a critical and financial success. In 2017, a TV series also based on Leonard’s novel premiered on Epix (now MGM+). — CA

Hitchcock/Truffaut
(Fran?ois Truffaut, 1967)

In a quarter-century or so of elementary, secondary, undergraduate and graduate schooling, no course cemented itself as firmly in my mind as USC professor Drew Casper’s exhaustive seminar on Alfred Hitchcock — thanks to the master of suspense himself, Casper’s lively lectures and this book. “Hitchcock/Truffaut” is the inimitable, and today inconceivable, product of a 50-hour interview in which the French filmmaker and critic pressed the idol of the Cahiers du Cinéma set “to reveal all his secrets.” The result exemplifies the politique des auteurs, or auteur theory, as thoroughly as any manifesto, but “Hitchcock” isn’t useful merely for its interest in the director’s “minor” works, or for the insights Truffaut draws out that no other interlocutor ever did. It is, above all, detailed proof that art, though subject to the forces of chance and the shifting winds of culture, is ultimately about choices. This star, this shot, this cut, this color: From such decisions the great masterpieces of Hollywood cinema are made. — Brennan

The Day of the Locust
(Nathanael West, 1939)

In West’s scabrous novel, Hollywood is a freak show fated to end in apocalypse, inhabited by deluded hangers-on convinced of their importance and unwilling to confront their mediocrity (West originally titled his book “The Cheated”). Yale-trained artist Tod Hackett, toiling as a studio scene designer, doesn’t just see the fire coming; he’s hard at work predicting and depicting it in a painting called “The Burning of Los Angeles.” But most of the characters have already seen their dreams burn down: Faye Greener, a beautiful but talentless actor; her father, an old vaudevillian reduced to peddling silver polish; and a host of other eccentrics and grotesques. For West, whose own screenwriting career was getting started when he died in a car crash in 1940, Hollywood was where the American Dream went to die. — CV


Play It As It Lays
(Joan Didion, 1970)

Maria Wyeth came to Hollywood for the same reason as the rest of us: to escape from someplace else. When we meet her in “Play It As It Lays,” though, the actor’s hometown of Silver Wells, since swallowed by a missile range in the Nevada desert, has regained a certain appeal, “the restorative power of desolation.” After all, her parents are dead, her marriage is disintegrating, her child is institutionalized, her career is in free fall. Only her father’s advice to her, that life itself is a crap game, has held up over time. “Everything goes,” she laments. “I am working very hard at not thinking about how everything goes.”
> GO TO STORY
Credits
Contributing editors: Carolyn Kellogg, Hanna Sender
Writers: Carlos Aguilar, Mark Athitakis, Manuel Betancourt, Matt Brennan, Carolyn Kellogg, David Kipen, Amy Nicholson, Chris Vognar
Senior deputy design director: Faith Stafford
Lead art direction and design: Kay Scanlon
Illustration: Golden Cosmos
Copy editors: Joan Fantazia, R. Marina Levario
Photo editor: Jerome Adamstein
Fact-checker/photo researcher: Michael Darling
...
Book credits
Amistad; Bloomsbury; Columbia University Press; Day Street Books; Ecco; Farrar, Straus & Giroux; Flatiron; Forever; Grand Central Publishing; Graywolf Press; Grove Press; Harper; Harper & Row; Henry Holt & Co.; Houghton Mifflin; It Books; Knopf; Knopf Doubleday; Marion Boyars; Newmarket Press; NYRB Classics; NYU Press; Pantheon; Penguin; Plume; Praeger; Random House; St. Martin’s Press; Scribner; Simon & Schuster; Straight Arrow Books; Twelve; University of Chicago Press; University of Minnesota Press; Vintage; Warner Books; William Morrow
Subscriber Exclusive Alert
If you're an L.A. Times subscriber, you can sign up to get alerts about early or entirely exclusive content.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.













